In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, understanding the nuances between different engineering methodologies is crucial. Two such methodologies, reverse engineering and forward engineering, play pivotal roles in the development and improvement of products. But what exactly are these processes, and how do they differ? Let’s dive in to explore the key differences and applications of reverse engineering and forward engineering.

What is Reverse Engineering?
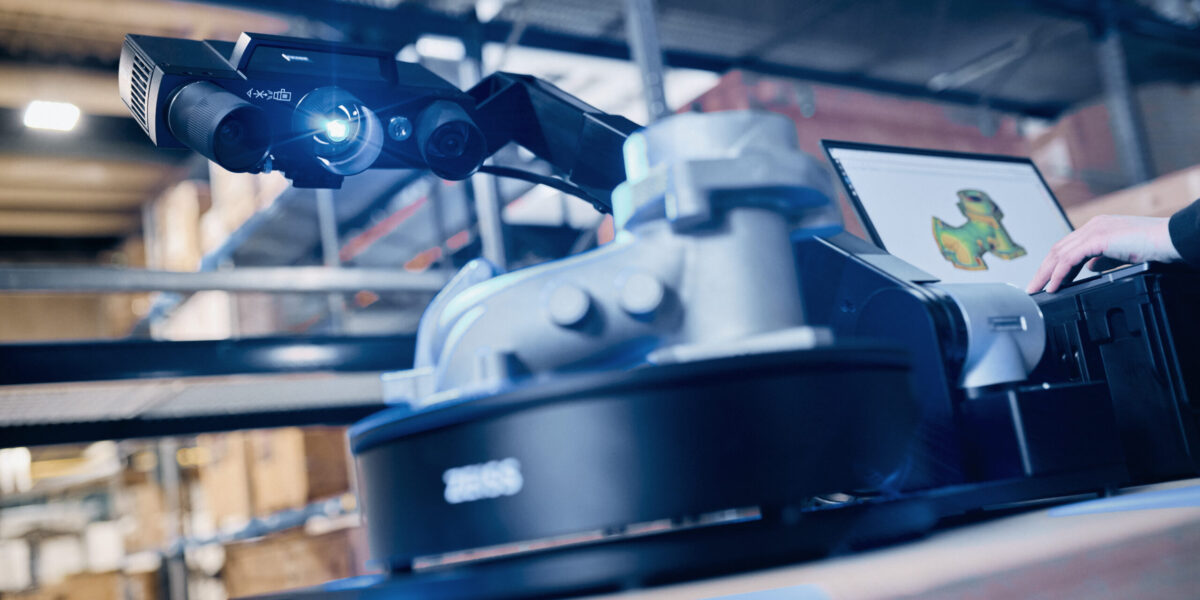
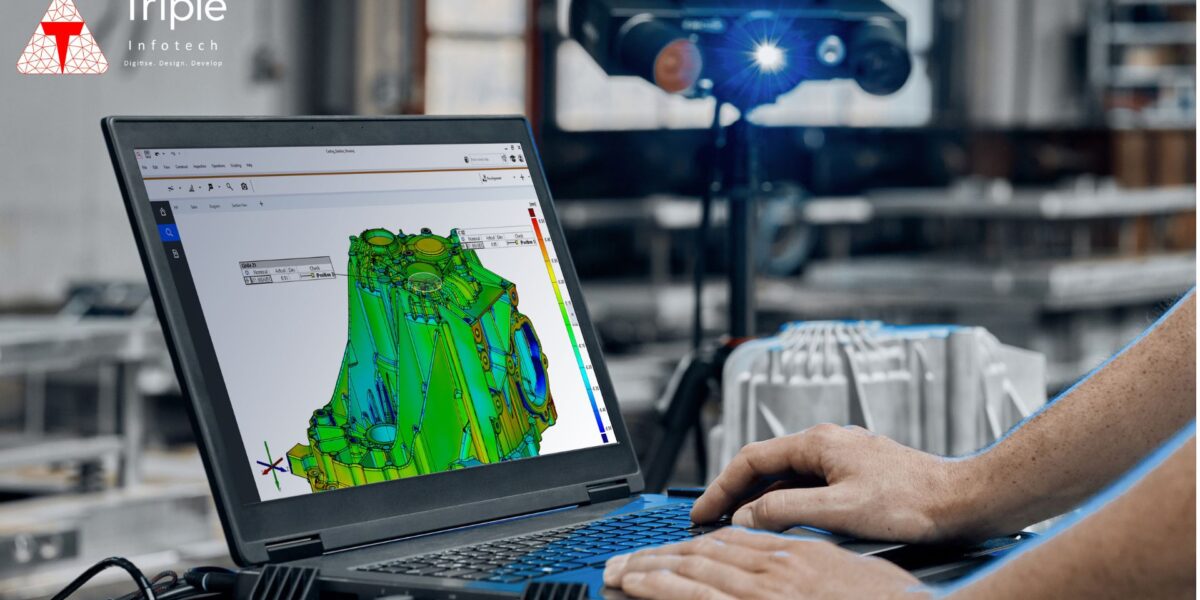
Reverse engineering is the process of deconstructing a product or system to understand its design, functionality, and operation. This process involves taking apart a physical object to learn about its components, materials, and construction methods. In essence, reverse engineering seeks to unravel the blueprint of an existing product.
Applications of Reverse Engineering
- Product Analysis: Companies often use reverse engineering to analyze competitors’ products. By understanding the design and materials, they can gain insights into how to improve their own products or identify potential patent infringements.
- Legacy Parts Recreation: Many industries rely on older machines or equipment that may no longer have readily available spare parts. Reverse engineering enables the recreation of these parts, ensuring continued operation and avoiding costly replacements.
- Quality Improvement: By examining a product’s design and identifying weaknesses or areas for enhancement, manufacturers can improve the quality and performance of their products.
- Cybersecurity: In software and hardware development, reverse engineering helps in identifying vulnerabilities and threats, allowing developers to enhance security measures.
What is Forward Engineering?
Forward engineering, on the other hand, is the traditional approach to product development. It involves designing a product from scratch based on specific requirements and specifications. This process typically starts with a conceptual design, followed by detailed engineering, prototyping, and testing, eventually leading to full-scale production.
Applications of Forward Engineering
- New Product Development: Forward engineering is the cornerstone of innovation. It allows companies to create entirely new products, pushing the boundaries of technology and design.
- Customization: When a company needs a product tailored to specific needs, forward engineering is the go-to method. This process ensures that the product meets all required standards and functionalities.
- System Upgrades: Forward engineering is often employed to upgrade existing systems, incorporating new features, technologies, or improvements that enhance overall performance.
Key Differences Between Reverse Engineering and Forward Engineering
| Aspect | Reverse Engineering | Forward Engineering |
| Purpose | To understand and replicate existing products | To create new products from initial concepts |
| Starting Point | Begins with a finished product or system | Starts with a concept or set of requirements |
| Process | Deconstructive; involves analyzing and breaking down | Constructive; involves designing and building up |
| Outcome | Replicated or improved version of an existing product | A new or updated product or system |
| Application | Used in product analysis, recreation, and improvements | Used in new development, customization, and upgrades |
When to Choose Reverse vs. Forward Engineering
The decision to use reverse engineering or forward engineering depends largely on the project’s goals and requirements:
- Use Reverse Engineering When:
- You need to analyze a competitor’s product to understand its strengths and weaknesses.
- There’s a need to recreate or improve an obsolete part or system.
- You want to enhance an existing product without starting from scratch.
- Cybersecurity analysis of software is required to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Use Forward Engineering When:
- Developing a completely new product or system.
- There’s a need to create a customized solution tailored to specific requirements.
- Upgrading an existing product with new features or technologies.
- Innovation and market leadership are the primary goals.
Conclusion
Both reverse engineering and forward engineering have their unique advantages and are integral to the product development cycle. Understanding the differences between these two methodologies can help businesses make informed decisions, optimize their processes, and ultimately deliver better products to the market.
At Triple Infotech, we specialize in providing cutting-edge 3D scanning services that support both reverse and forward engineering processes. Whether you’re looking to recreate a legacy part or develop a new product from scratch, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist with your engineering needs!





I am extremely inspired with your writing abilities and also with
the structure for your weblog. Is that this a paid subject matter or
did you modify it your self? Either way keep up the excellent quality writing,
it is uncommon to peer a great weblog like this one nowadays.
Lemlist!
What you’ve written here is not just insightful — it’s comforting. There’s a warmth to your words that makes the reader feel seen and understood, as though you’re sharing something deeply personal and valuable. This is the kind of writing that stays with you long after you’ve finished reading it.